Install System Software
netlab install uses internal installation scripts to install nice-to-have Ubuntu software, Ansible and related networking libraries, or libvirt+vagrant.
The ubuntu, libvirt, and containerlab installation scripts run only on Ubuntu[1] and Debian[2]; the ansible and grpc installation scripts should run in any environment with bash and pip3.
Usage
netlab install -h
usage: netlab install [-h] [-v] [-q] [-y] [-u] [--all] [script ...]
Install additional software
positional arguments:
script Run the specified installation script
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-v, --verbose Verbose logging
-q, --quiet Be as quiet as possible
-y, --yes Run the script without prompting for a confirmation
-u, --user Install Python libraries into user .local directory
--all Run all installation scripts
Run "netlab install" with no arguments to get install script descriptions
Tip
Running multiple installation scripts with netlab install or netlab install –all might fail on some Ubuntu distributions due to background processes locking the APT repository directory. If you experience that problem, execute multiple netlab install commands (one per installation script).
Installation Scripts
The ubuntu script installs Python3 development components that might be needed for Ansible installation, common tools like git and sshpass, and XML libraries.
The libvirt script installs libvirt and supporting libraries/packages, vagrant, vagrant-libvirt plugin, and creates the vagrant-libvirt virtual network.
The containerlab script installs Docker Engine and containerlab.
The ansible script uses pip3 to install the latest version of Ansible, networking libraries (netaddr, paramiko, netmiko), text parsing libraries (testfsm, ttp, ntc-templates), and a few other utility libraries (jmespath, yamllint, yq)
The graph script installs GraphViz and D2 software needed to generate graphs from netlab topologies
The grpc script installs gRPC Python libraries needed to configure Nokia SR Linux and Nokia SR OS.
You can display an up-to-date list of installation scripts with netlab install command:
$ netlab install
┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓
┃ Script ┃ Installs ┃
┡━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┩
│ ubuntu │ Mandatory and nice-to have Debian/Ubuntu packages │
│ libvirt │ QEMU, KVM, libvirt, and Vagrant │
│ containerlab │ Docker and containerlab │
│ ansible │ Ansible and prerequisite Python libraries │
│ grpc │ GRPC libraries and Nokia GRPC Ansible collection │
│ graph │ GraphViz and D2 software │
└──────────────┴───────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
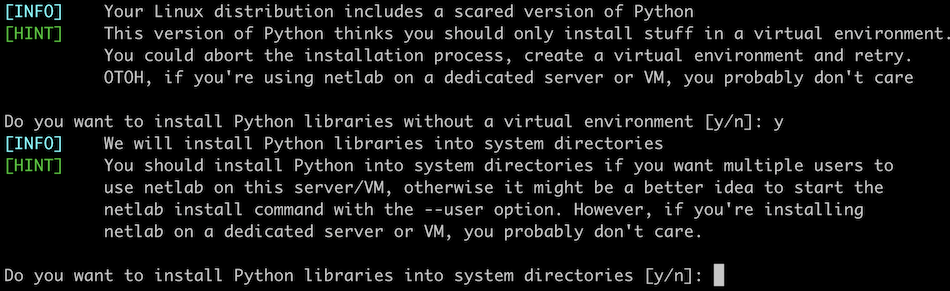
Python Package Installation
Unless you started the netlab install command in a Python virtual environment, it runs pip3 as root. You can change that default with the -u option, asking netlab install to install Python packages into the ~/.local directory.
Newer Python installations (including Ubuntu 22.04) refuse to install Python packages outside a virtual environment. In these cases, netlab install asks the user for a confirmation and uses --break-system-packages pip3 option to force user-wide or system-wide package installation: